All published articles of this journal are available on ScienceDirect.
A Novel Approach to Simulate a Charge Transfer in DNA Repair by an Anacystis nidulans Photolyase
Abstract
An Anacystis nidulans photolyase enzyme containing two chromophore cofactors was simulated for a photoreaction DNA repairing process via molecular dynamics (MD) method. A novel approach has been introduced for the electron transfer between the FAD (flavin adenine dinucleotide; flavin) molecule and CPD (cyclobutane pyrimidine dimer). This approach involves four simulation stages with different charges for the FAD and CPD fragments and a role of a charged state of the active cofactor was qualified during the MD modeling. Observations show that flavin has actively participated in a charge transfer process, thereby involving the conformational changes of the DNA and CPD substrate fragment. The DNA conformation behavior has shown to correlate with the electron transfer from flavin to CPD. This is manifested on the similarities of the DNA repairing process by excision repair of the UV photoproducts.
1. INTRODUCTION
Photolyases (PHTs) are unique DNA repair enzymes (monomeric protein of 450-550 amino acids), which as light-dependently catalyzing agents serve in conversion mechanism of damaged photoproducts (PPs) to original state. For today three crystal structures of the DNA PHTs are known [1-3]. There are two types of DNA damages: cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers (CPDs) and (6-4) photoproducts ((6-4) PPs) [4]. (We imply thymine dimers, Pyr<>Pyr, for the CPDs, and Pyr[6-4]Pyr for pyrimidine-pyrimidone (6-4) PPs). The PHTs repair the CPD and (6-4) PPs, herewith recovering back the damaged DNA to its original (native) state. The mechanism of the CPD lesion recognition and binding have been described in literature throughout the biochemical data [5, 6], computer modeling [1, 7, 8], nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy [9] and so on. According to these data the PHTs flip the damaged di-nucleotide out of the DNA double helix into its own active site, performing next a substrate binding. Following the photon absorbing through its antenna the PHT pigment triggers the excitation energy transfer to a catalytic cofactor which is called FAD (flavin adenine di-nucleotide) (see Fig. 1). Between the catalytic active FAD (shortly, flavin) and CPD the exchange of an excessive energy for the repairing of the damaged di-nucleotide occurs. The CPD repair thus results into splitting of two pyrimidines to an original shape. As a final reaction step, the electron charge is transferred back to flavin, thereby is restoring a flavin’s catalytically active form.
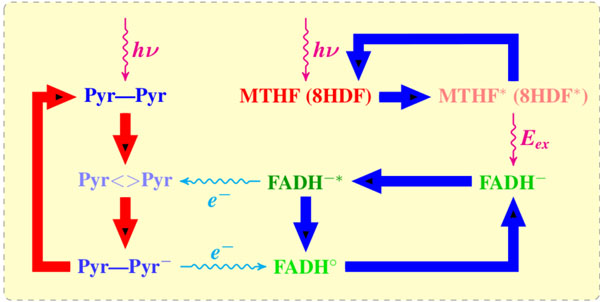
A reaction mechanism of blue light-mediated repair of CPD lesion by DNA PHTs (photolyases). The UV influence damages the DNA neighboring pyrimidines (Pyr–Pyr) and induces a CPD (Pyr<>Pyr) lesion. The cofactor (MHTF or 8-HDF) adsorbs light photon and transfers it to a catalytically active flavin (FADH–) as an excitation energy Eex via dipole–dipole interaction. The flavin molecule (FADH-*) transfers an electron to CPD. The CPD splits out into two pyrimidines, thereby transferring back the electron to a newly formed FADHo; in its final state the flavin molecule has to pass into a catalytically active form.
Described above the DNA repairing mechanism works in certain organisms that possess a photoreactivating PHT enzyme inside. The enzyme contains two chromophores which are capable for capturing photons from the UV-B (ultraviolet blue) light of a wavelength between 350-450 nm. The PHT detects, recognizes and binds the damaged DNA (a DNA’s CPD site). The light energy in a visible range (350-450 nm) is being absorbed by a light-harvesting cofactor 5,10-Methylenetetrahydrogolate (MTHF) or 8-hydroxy-7,8-didemethyl-5-deazari-boavin (8-HDF). The adsorbed energy is used in the oxidation of a cyclobutane ring, and, subsequently, in conversion of thymine’s dimmer into two separate monomers. As a result, the PHT enzyme dissociates from the DNA, so the damage is thus repaired.
It is worth noting that the CPD recognition process by the PHT does not influence the content of the DNA nucleotides. More details of the DNA repair by PHTs could be found in [10] where the PHT mechanism has been found in prokaryotes, lower and higher eukaryotes. Nevertheless, the PHT existence in placental mammals is still unknown.
The CPD repair mechanism in human takes place through the excision repair occurs in dark conditions [10, 11]. The excision repair does not require light; the PHT instead of repairing the breaking bonds only recognizes where the region of damaged nucleotides is located. The protein complex recognizes the distortion of the DNA molecule (CPDs), so related DNA strand with its CPD to be cut off. Generally, 12 nucleotides could be recognized and a DNA part with its marked chain could be removed. A DNA polymerase-I [12] fills up the gap and a DNA ligase [13] removes the recognized part. Other DNA repair mechanism includes mutagenic repair or dimer bypass, recombination repair, cell-cycle checkpoints, apoptosis and certain alternative repair pathways and so on. The above mentioned mechanism can be operative in various organisms that involve the CPDs or (6-4) PPs correction process [14]. The DNA repair process has also been reviewed in [15], where the crystal structures of the replicative and bypass DNA polymerases were encountered. Thereby two typical lesions arising from the oxidation of DNA were distinguished.
The UV damages on the DNA are generally responsible for the induction of skin tumors, the formation of cell carcinomas and melanomas [16]. The UV induced dimmers for the DNA could brought a mispairing of DNA strands, so far, the induced damage in the next stage of DNA copying can stop a precise programmed replication altogether. Unless the DNA damage is repaired the pyrimidine dimers can lead to a transcription blocking, to various mutations or to a cell death finally, thereby originating a cancer disease [17].
2. STRUCTURE
All PHTs contain two noncovalently bounded chromophores (cofactors). First chromophore is a catalytic flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD or flavin). It is worth noting that FAD (flavin) is an essential cofactor regarding the light-dependent repair process [18]. The second is a light-harvesting cofactor which can be either methenyltetrahydro-folic acid (MTHF or pterin) present in Escherichiacoli (E. coli) photolyase or 8-hydroxy-5-deazaflavin (8-HDF or deazaflavin) found in Anacystis nidulans (A. nidulans) [2, 4, 11, 19, 20]. The thermostable photolyase from Thermus thermophilus (T. thermophilus) has favorable functions even without of the second cofactor [3].
In the present study we simulate the deoxyribodpyrimidine PHT protein A. nidulansvia molecular dynamics (MD) method. In Fig. (2) the amino acids sequence for the PHT A. nidulans protein is presented.

The secondary amino acid sequence of A. nidulans photolyase. A secondary structure element has shown as α-helices (blue), β-strands (magenta) and 310-helices (cyan). Highlighted amino acids involved the binding of FAD (red) and 8-HDF (green) regions.
The nucleotide sequences of simulated DNA structures are shown in Fig. (3).

Flipped-out after repair and CPD-like DNA nucleotides sequences.
It is worth noting that the crystal structure of A. nidulans enzyme was obtained and studied in [2, 11, 19, 21]. Figs. (4 and 5) below demonstrated the A. nidulans crystal structure where a ribbon diagram representation includes the α-helices, β-strands and 310-terminals in different colors. The structure of this protein was taken from the Protein Data Bank (PDB ID: 1TEZ). Until now, we have introduced several structures for the flipped-out CPD-like DNA, so as to investigate the damaged and repaired states of the DNA molecule by the PHT enzyme.
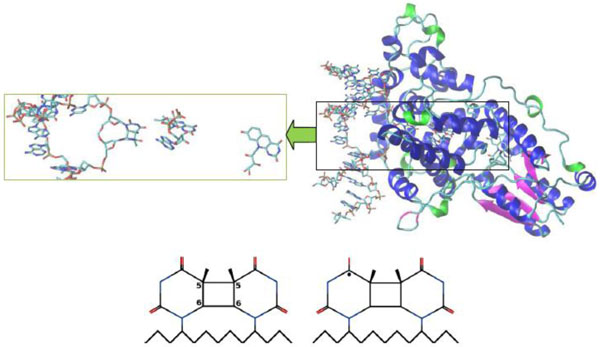
Crystal structure of A. nidulans photolyase with different DNAs (CPD substrate). The β-strands are colored in magenta, the α-helices are in blue and the 310-helices are in green. The CPD substrates correspond to (00) and (01) configurations, respectively. The first substrate (bottom, left) is an electron acceptor; after accepting the electron from FAD it will be transformed into the second form (bottom, right). A neutral flavin is FADH-*, a positively charged flavin is FADHo.
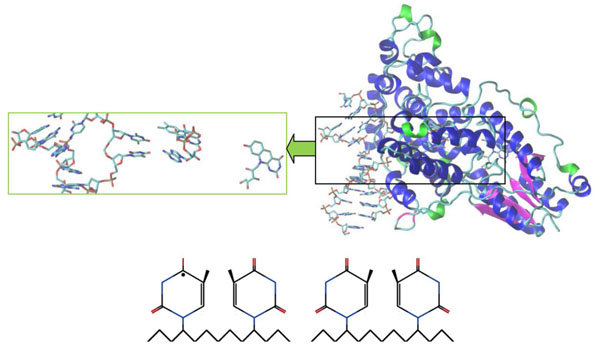
Crystal structure of A. nidulans photolyase with different DNAs (repaired CPD-like substrate). The CPD-like substrates are (11) and (10) configurations, respectively. The first substrate (11) is left (bottom), the second (10) is right (bottom). The electron transfer causes the splitting of the dimer into an original shape, so it becomes an electron donor. The electron transfers back to a flavin which transforms the CPD-like substrate into a required nucleoside pair (from FADHo to FADH-). A positively charged flavin is FADHo, a neutral flavin is FADH-.
3. PHT-DNA CHARGE TRANSFERRING MODEL BUILDING
For the MD simulation we have used Amber 11 software package with AmberTools 1.5 module [22]. The two sets of models describing various charge distribution scenario during the PHT-DNA interaction were introduced. The PHT-DNA charge transfer has been simulated as a two stage process which is: (1) Dynamics in CPD repair; (2) Dynamics in after CPD repair. For the two-stage process we built two sets of molecular configurations as: (1) Models (00) and (01); (2) Models (11) and (10). Here in (00), (01), (10) and (11) models are the first index stands for a CPD state, the second one for a flavin charge. For example, in notation (10) index 1 means a CPD repaired state, 0 means a neutral state of the flavin molecule; in (01) index 0 means a damaged CPD state; 1 – flavin charged molecule, respectively. For all configurations we have simulated the same protein and cofactors.
A CPD-containing DNA structure was different for existing pairs as illustrated in Fig. (3) (The two CPD-containing DNA structures are presented). Also, for the first configuration pair ((00) and (01)) the charges of flavin are different: neutral flavin is FADH-*; positively charged flavin is FADHo (Fig. 1). For the second configuration pair ((10) and (11)) that are true after CPD repairs within DNA, the flavin charge is different: positively charged flavin is FADHo; a neutral flavin is FADH- (Fig. 1). In Figs. (4 and 5) the related PHT-DNA configurations with corresponding CPD substrates are shown.
In a neutral flavin the charge on atom N1 is equal to q(N1) = – 0.1006. Changing q(N1) from – 0.1006 to + 0.8994 has brought flavin to a positively charged state. We have manually changed the charge on atom N1 to simulate the different flavin’ charge states, in correspondence to the CPD repair reaction mechanism as shown in Fig. (1). At the same time, for a neutral CPD we have the following charges on atoms O4T and C4T: q(O4T) = – 0.5715 and q(C4T) = + 0.7075. Subsequently, changing q(O4T) from – 0.5715 to – 1.0715 and q(C4T) from + 0.7075 to + 0.2075 brought CPD to a negatively charged state.
The MD calculations on four molecular configurations ((00), (01), (10), and (11)) were completed during 3 ns dynamical changes. The flavin and CPD structures were restrained; the weights of the positional restraints varied from 0.0 to 0.005 kcal/mol·Å. The Langevin dynamics temperature regulation was used with the parameters TEMP0 = 300, IG = 71277 and the collision frequency γ = 2 ps–1 [23-25]. For the bond length constraints the SHAKE algorithm [26] with parameter NTC = 2 was used for the default relative geometrical tolerance of coordinate resetting.
4. RESULTS AND DATA ANALYSIS
For the PHT-DNA interaction process the two sets of molecular configurations were simulated and their comparative analysis was performed. Herewith we have introduced both neutral and negatively charged CPD-substrates. For the configurations (00) and (10) both flavin and CPD are neutral. The difference is that in (00) model two adjusted thymines are connected together (a damaged DNA), but in (10) model the adjusted thymines are already separated (a repaired DNA). During the DNA repairing process, that is in the (01)→(11) transition, we have both flavin and CPD substrate as charged molecules. In this process, viz. (01) and (11) states, flavin has charged positively, but CPD – negatively. So far, the configurations (00) and (01) describe the flavin-CPD charge transfer process; for the (11) and (10) states one has a return process – CPD transfers its electron back to the flavin.
4.1. Dynamics in Repair
It is known that the electron transfer can occur any moment of time, when the distance between the atoms CPD[O4T]–FAD[N6A] is less than 5-10 Å [8, 27, 28].
The first object of our interest was the dynamics of the flavin (FADH-*) and CPD (Pyr<>Pyr) exchange. Simu-lations with configuration (00) observe the interaction of these two components as a donor (flavin) and an acceptor (CPD); the behavior of this interaction should be the predominant one. The MD results for configuration (00) are shown in Figs. (6) (left and right diagrams). Left diagram in Fig. (6) shows the RMSD (root mean-square displacements) results for the CPD, flavin (FAD) and DNA, respectively. Right diagram of Fig. (6) shows the distance calculation results that illustrate the flavin-CPD exchange dynamics. The distance diagram was constructed for the flavin’s oxygen and protein’s TYR225 (OH); it is worth noting that TYR225 is nearby to FAD amino acid residues (Fig. 2).
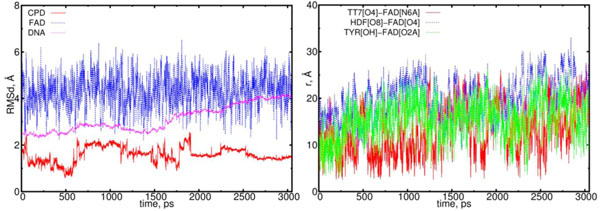
The RMSD and distance distribution data for the (00) model. On the left, the RMSD are presented for the neutral flavin (blue), neutral CPD (red) and DNA (magenta). On the right, the interatomic distances are presented for the FAD-(CPD, HDF, TYR225). The RMSD of the DNA molecule gradually increases from 2.5 up to 4.0 Å. The CPD substrate sharply fluctuates with the 1.5 Å amplitude within the time interval from 0.5 to 2 ns. The interatomic distance between the flavin and CPD becomes closer in the intervals of t = 0.0 to 0.3 ns, 0.5 to 1.3 ns, 1.7 to 1.9 ns and 2.1 to 2.6 ns (red curve; right diagram). The distance between the flavin’s oxygen and HDF (O8), protein’s TYR225 (OH) demonstrate the flavin’s oscillation degree and its positional changes in the interaction process (blue and green lines).
Flavin has been an essentially mobile molecule (blue curve in Fig. 6) which oscillates periodically around its equilibrium position. Flavin’s motion eventually influences the CPD conformational behavior. For the (00) state the flavin-CPD exchange results in the rotating of DNA around its symmetrcal axis. Nevertheless, the DNA conformation in (00) model does not change visibly. But the CPD conformation due to a strong interaction with flavin essentially changes; the CPD dynamics has observed to be stabilized only after t = 2.5 ns.
In Fig. (7) the RMSD and distance distribution results are presented for the (01) model. In (01) model the FADHo-CPD interaction does not follow a donor-acceptor type. After charge transferring, the flavin-CPD interaction comparing with (00) model weakens. The main feature of the flavin-CPD interaction for the (01) model is that the flavin-CPD distance holds large values (more than > 9 Å) from t = 0 to 1.5 ns. This should be compared with the (00) case where flavin reaches CPD closely to distances < 5 Å in the interval of t = 0 to 1.5 ns. In (01) model the DNA molecule does not turn rotate its symmetrical axis, but it tilts to a flavin’s positional side. Therefore, the CPD shape in the (01) model looks like as a deformed one.
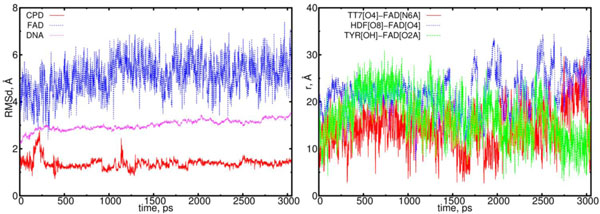
The RMSD and distance distribution data for the (01) model. On left, the RMSD are presented for the positively charged flavin (blue), negatively charged CPD (red) and DNA (magenta). On the right, the interatomic distances are presented for the FAD-(CPD, HDF, TYR225). The RMSD of the DNA remains stable around 3.0 Å. The RMSD of the CPD sharply fluctuates only at the start of simulation, however, at later stages (at > 1.2 ns) it stabilizes. The interatomic distance between the flavin and CPD becomes closer but slightly (from t = 1.5 to 2 ns (red)).
In Fig. (8) the configuration snapshots of the DNA molecule are presented. Fig. (8) shows the snapshots of the CPD-containing DNA for the models (00) and (01), respectively. In correlation with the RMSD and distance distribution data (Figs. 6 and 7), the CPD fragment inside the DNA follows two different dynamical scenarios. Starting from the same state at t = 0.0 (in center) at later stages of the dynamics, at t = 1.5 ns (the first configurations from the center: (00)-left, (01)-right) and 3.0 ns (the edge configurations from the center: (00)-left, (01)-right), we have two different DNA (CPD) conformational shapes. The positional and structural changes of the CPD fragment inside the DNA molecule are straightforward.
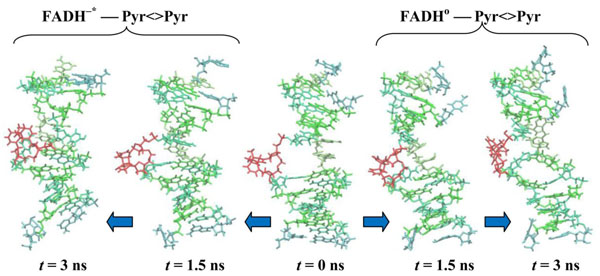
CPD-containing DNA molecule changes during simulations. CPD-fragments are shown at t = 0.0 (center), 1.5 (first from the center) and 3.0 ns (outside). The DNA positions are shown from the center to the left for the (00) model, from the center to the right for the (01) model.
4.2. Dynamics After Repair
The electron transfer causes the cleavage of the 5-5 and 6-6 bonds of the CPD substrate. In (11) model the flavin and CPD-like substrate Pyr–Pyr (where two adjusted thymines are being separated) can form the acceptor-donor configuration pair. Unlike (00) configuration in (11) model a donor is a CPD-like substrate, but the acceptor is flavin. One thymine has been separated from the CPD interacts with adjusted thymine through its excess electron. This causes each thymine to be differently oriented, thereby repulsing each other within a distance larger than standard nucleoside-nucleoside ones. The DNA configuration during the simulation in (11) model exhibits a clear repulsive process between two adjusted thymines, so at final (3 ns) state they oriented in opposite directions. The DNA molecule subjected by a flavin-substrate interaction rotates around its symmetrical axis. The RMSD and distance distribution data for the (11) model are presented in Fig. (9); the detailed interpretations are followed on the caption.
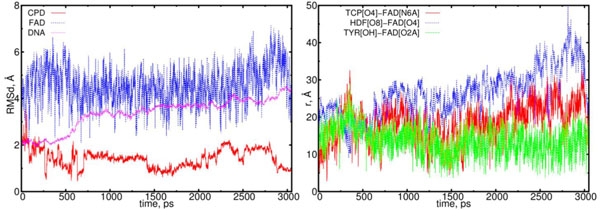
The RMSD and distance distribution data for the (11) model. On the left, the RMSD are presented for the positively charged flavin (blue), negatively charged CPD-like substrate (Pyr–Pyr) (red) and DNA (magenta). On the right, the interatomic distances are presented for the FAD-(CPD, HDF, TYR225). The RMSD of the DNA molecule essentially increases from 2.0 up to 4.5 Å. The CPD-like substrate (Pyr-Pyr) decreases at the start of simulation run, sharply fluctuates between 0.75 and 2 ns. The interatomic distance between the flavin and CPD-like substrate becomes closer in the intervals of t = 0.5 to 0.75 ns, and 1.25 to 1.75 ns (red curve; right diagram). The distance between the flavin’s oxygen and HDF (O8), protein’s TYR225 (OH) demonstrates that flavin has kept its position close to protein (blue and green lines).
Finally, in Fig. (10) the MD results are presented for the (10) model. In (10) configuration the CPD-like substrate (Pyr–Pyr) does not seems to interact with the flavin molecule actively. In (10) model the electron has already been transferred from CPD-like structure to flavin. So far, during the simulations both thymines are observed to be rotated inward the DNA structure to hide in. This process shows a trend how the repaired DNA structure behaves being normal.
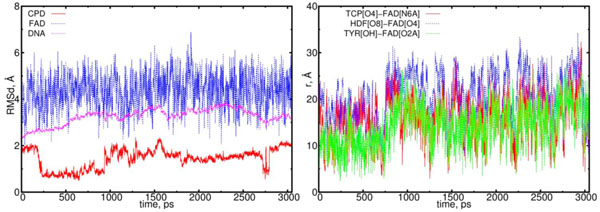
The RMSD and distance distribution data for the (10) model. On left the RMSD are presented for the neutral flavin (blue), neutral CPD-like substrate (Pyr–Pyr) (red) and DNA (magenta). On right the interatomic distances are presented for the FAD-(CPD, HDF, TYR225). The RMSD of the DNA molecule reach a plato of 2.5 Å, thereby indicating on a stabilization process. The CPD-like substrate (Pyr–Pyr) fluctuates from the start, but it stabilizes after 1.6 ns. The interatomic distance between the flavin and CPD-like substrate becomes closer till t = 0.75 ns, and from 1.25 to 2.25 ns (red curve; right diagram). The distance between the flavin’s oxygen and HDF (O8), protein’s TYR225 (OH) demonstrates the flavin’s shifting from its equilibrium position (blue and green lines).
In Fig. (11) the configuration snapshots of the DNA molecule are presented. Fig. (11) shows the snapshots of the CPD-like substrate inside DNA for the models (11) and (10), respectively. Starting from the same state at t = 0.0 (in center) the CPD-like substrate in model (11) shows a repulsive behavior of the adjusted thymine (left); but in model (10) these adjusted thymines do not repulse each other any further as they tend to hide inside the DNA chain (right). The positional and structural changes of the CPD-like fragment inside the DNA molecule could be compared at t = 1.5 ns (the first configurations from the center: (11) – left, (10) – right) and 3.0 ns (the edge configurations from the center: (11) – left, (10) – right).
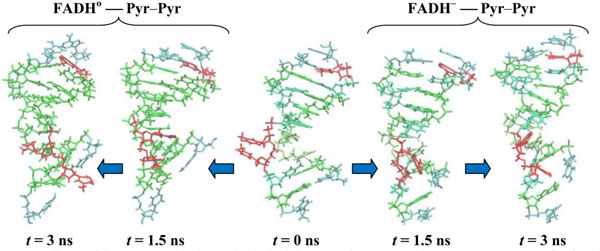
CPD-like-containing DNA molecule changes during simulations. CPD-fragments are shown at t = 0.0 (center), 1.5 (first from the center) and 3.0 ns (outside). The DNA positions are shown from the center to the left for the (11) model, from the center to the right for the (10) model.
The nucleotide pair interactions observed in [29, 30] report the recent crystal structures of the human cleavage factor (CFI(m)25 homodimer) in complex with UGUAAA and UUGUAU RNA sequences. [29, 30] demonstrate that the CFI(m)25 is both necessary and sufficient for the sequence-specific binding of the poly(A) with UGUA element. In these works the crystal structure of CFI(m)25 complex with the RNA recognition motif (RRM) domain are well studied.
5. CONCLUSION
A novel approach described above may serve as a useful tool for understanding molecular mechanism of DNA repair of the UV photoproducts. The MD simulations for a charge transfer mechanism with A. nidulans enzyme provide a new glance for the DNA repair and could easily be extended for the electron transfer process, specifically for the FAD and CPD fragments. The PHT-DNA charge transfer was simulated as a two-stage process (dynamics in and after CPD repair), thereby constructing four charge exchange models: two stands for a repairing stage, two – for an after repair ones.
Dynamics in CPD repair is the interaction exchange between the flavin (FADH-*) and CPD (Pyr<>Pyr, where two adjusted thymines are together), which are described by models (00) and (01). Simulations with configuration (00) observed the interaction of these two components as a donor (flavin) and an acceptor (CPD) and the behavior of this interaction as the predominant one. Flavin as being essentially mobile molecule oscillates around its equilibrium position, thereby influencing a CPD conformational behavior. For the (00) state the flavin-CPD exchange results as on the DNA rotating around its symmetry axis; the DNA conformation in (00) model does not visibly change. But the CPD conformation due to a strong interaction with flavin changes essentially.
Dynamics after CPD repair is the interaction exchange between the flavin (FADH-) and CPD-like substrate (Pyr–Pyr, where two adjusted thymines are separate), which are described by models (11) and (10). The electron transfer causes the cleavage of the 5-5 and 6-6 bonds of the CPD substrate. The DNA configuration during the simulation in (11) model exhibits a clear repulsive process between two adjusted thymines. In (10) model the electron has already being transferred from CPD-like structure to flavin and ad-justed thymines observed rotated inward the DNA structure. The process looks like as how the repaired DNA structure behaves in a normal state.
In conclusion, the DNA-PHT conformation as global structural behavior could be detected only through the atomistic/molecular simulation that ones has employed. Until now for such complex multiparticle system, as PHT enzyme interacting with DNA, performing more precise quantum chemistry calculations seem to be quite a challen-ging task. The DNA conformational change are subjected to differences on the charge distribution between the DNA and PHT. During the MD modeling of present study this main feature was taken into account and the results were compared between the different scenarios in the charge states.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors confirm that this article content has no conflicts of interest.
PATIENTS CONSENT
Informed Consent was given to the Author by the patients in respect of the clinical trials conducted.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was jointly supported by the JSPS (Japan Society for the Promotion of Science) and the RFBR (Russian Foundation for Basic Research); Grant No. 13-04-92100.


